Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects". The object contains both data and code.
Data in the form of properties (often known as attributes), and code, in the form of methods (actions the object can perform).
An object has the following two characteristics:
Attribute
Behavior
For example, A Car is an object, as it has the following properties:
name, price, and color as attributes
breaking, acceleration as behavior
Class and Objects
A class is a blueprint for the object. To create an object we require a model or plan or blueprint which is nothing but class.
For example, you are creating a vehicle according to the Vehicle blueprint (template).
The plan contains all dimensions and structures. Based on these descriptions, we can construct a car, truck, bus, or any vehicle. Here, a car, truck, bus are objects of Vehicle class
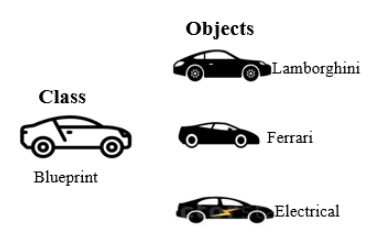
A real-life example of class and objects.
Class: Person
State: Name, Sex, Profession
Behavior: Working, Study
Using the above class, we can create multiple objects that depict different states and behavior.
Object 1: Jessa
State:
Name: Jessa
Sex: Female
Profession: Software Engineer
Behavior:
Working: She is working as a software developer at ABC Company
Study: She studies 2 hours a day
Constructors in Python
In Python, a constructor is a special type of method used to initialize the object of a Class. The constructor will be executed automatically when the object is created.
The __init()__ method is called the constructor in Python. In other words, the name of the constructor should be __init__(self).
Destructor in Python
object-oriented programming, A destructor is called when an object is deleted or destroyed. Destructor is used to perform the clean-up activity before destroying the object, such as closing database connections
The special method __del__() is used to define a destructor.
Encapsulation in Python
In Python, encapsulation is a method of wrapping data and functions into a single entity. For example, A class encapsulates all the data ( methods and variables).
Encapsulation acts as a protective layer.
We can restrict access to methods and variables from outside, and It can prevent the data from being modified by accidental or unauthorized modification.
Polymorphism in Python
Polymorphism in OOP is the ability of an object to take many forms. In simple words, polymorphism allows us to perform the same action in many different ways.
For example, The student can act as a student in college, act as a player on the ground, and as a daughter/brother in the home. Another example in the programming language, the + operator, acts as a concatenation and arithmetic addition.
Inheritance In Python
In an Object-oriented programming language, inheritance is an important aspect. In Python, inheritance is the process of inheriting the properties of the parent class into a child class.
The primary purpose of inheritance is the reusability of code. Using inheritance, we can use the existing class to create a new class instead of recreating it from scratch.
Here is the link to some questions about OOP
https://github.com/pushprajsinghrathore/ATM-working-on-OOPS-concept/blob/main/OPPS%20questions.ipynb
